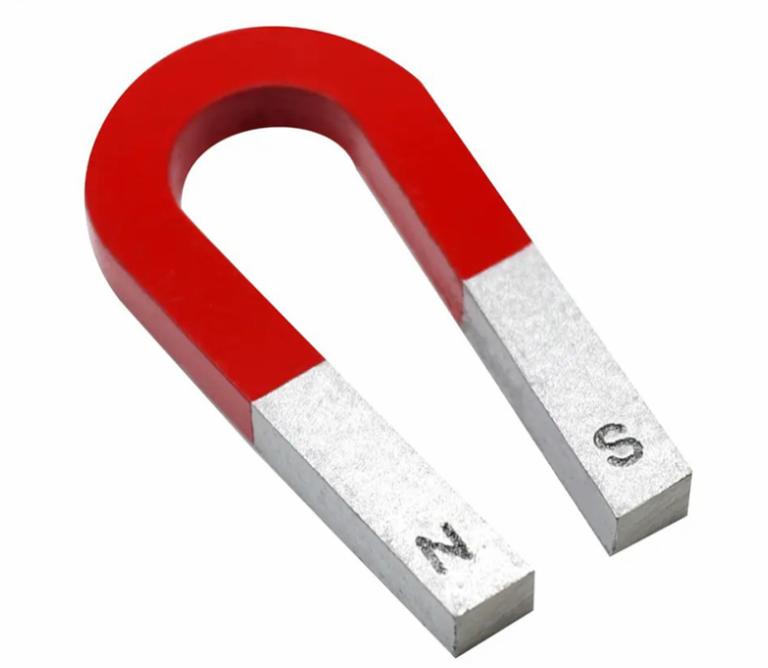
Ferrite Magnets
Ferrite is the most widely used permanent magnetic material, manufactured through powder metallurgy. It is mainly divided into two types: barium ferrite (Ba) and strontium ferrite (Sr), further categorized into anisotropic and isotropic varieties. It is a permanent magnetic material that is resistant to demagnetization and corrosion, with a maximum operating temperature of up to 250 degrees Celsius. Ferrite is hard and brittle, and it can be cut and processed using tools such as diamond sand. Alloy molds can be used for one-time molding. These products are extensively utilized in fields such as permanent magnet motors and speakers.
- Ferrite magnets belong to sintered permanent magnetic materials, composed of barium and strontium ferrite. In addition to having strong resistance to demagnetization, this type of magnetic material also offers the advantage of low cost. Ferrite magnets are hard and brittle, requiring special mechanical processing techniques. The magnetic energy product ranges from 1.1 MGOe to 4.0 MGOe. Due to their low cost, ferrite magnets have a wide range of applications, from motors and speakers to toys and crafts, making them the most widely used permanent magnetic material at present.
- Performance: Ferrite magnets are divided into isotropic and anisotropic types. Isotropic magnets, lacking orientation, can be magnetized in any direction, while anisotropic magnets, oriented along the manufacturing direction, need to be magnetized along the chosen direction. Anisotropic magnets have stronger magnetic properties than isotropic ones. Common performance grades for anisotropic magnets include Y25, Y30, Y35, Y30BH, etc.; while isotropic magnets commonly use performance grades such as Y8T, Y10T.
- Dimensions: Available in square, circular, ring, tile, and anisotropic shapes, which can be customized according to customer requirements.
- Processing: Square magnets can be wire cut or molded, while magnets of other shapes can only be molded.
Professional in producing magnets, Genesis New Journey is one of the best suppliers in China. We have quality Ferrite magnets for sale. Please feel free to contact us.
Looking for a certain size? If you require a specific size that is not available on our website, please contact us for a custom magnet quote.
Physical property
| Item | Unit | Parameter Range |
| Curie Temperature | ℃ | 450 |
| Maximum operating temperature | ℃ | 250 |
| Vickers Hardness | HV | 480-580 |
| Density | g/cm3 | 4.8-4.9 |
| Temperature coefficient of Br | %/℃ | -0.2 |
| Temperature coefficient of iHc | %/℃ | 0.3 |
Magnetic properties

| Permanent ferrite magnet standard | ||||||||
| Grade | Br | Hcb | Hcj | (BH) max | ||||
| MT | Gs | KA/m | Oe | KA/m | Oe | KJ/m3 | MGOe | |
| Y8T | 200-235 | ≥2000 | 125-160 | ≥1570 | 210-280 | ≥2610 | 6.5-9.5 | ≥0.8 |
| Y22H | 310-360 | ≥3100 | 220-250 | ≥2770 | 280-320 | ≥3520 | 20.0-24.0 | ≥2.5 |
| Y25 | 360-400 | ≥3600 | 135-170 | ≥1700 | 140-200 | ≥1760 | 22.5-28.0 | ≥2.8 |
| Y26H-1 | 360-390 | ≥3600 | 200-250 | ≥2512 | 225-255 | ≥2830 | 23.0-28.0 | ≥2.9 |
| Y26H-2 | 360-380 | ≥3600 | 263-288 | ≥3300 | 318-350 | ≥4000 | 24.0-28.0 | ≥3.0 |
| Y27H | 350-380 | ≥3500 | 225-240 | ≥2830 | 235-260 | ≥2950 | 25.0-29.0 | ≥3.1 |
| Y28 | 370-400 | ≥3700 | 175-210 | ≥2200 | 180-220 | ≥2260 | 26.0-30.0 | ≥3.3 |
| Y28H-1 | 380-400 | ≥3800 | 240-260 | ≥3020 | 250-280 | ≥3140 | 27.0-30.0 | ≥3.1 |
| Y28H-2 | 360-380 | ≥3600 | 271-295 | ≥3400 | 382-405 | ≥1800 | 26.0-30.0 | ≥3.3 |
| Y30H-1 | 380-400 | ≥3800 | 230-275 | ≥2890 | 235-290 | ≥2950 | 27.0-32.5 | ≥3.4 |
| Y30H-2 | 395-415 | ≥3950 | 275-300 | ≥3460 | 310-335 | ≥3900 | 27.0-32.0 | ≥3.4 |
| Y32 | 400-420 | ≥4000 | 160-190 | ≥2010 | 165-195 | ≥2070 | 30.0-33.5 | ≥3.8 |
| Y32H-1 | 400-420 | ≥4000 | 190-230 | ≥2390 | 230-250 | ≥2890 | 34.5-35.0 | ≥4.0 |
| Y32H-2 | 400-440 | ≥4000 | 224-240 | ≥2810 | 230-250 | ≥2890 | 31.0-34.0 | ≥3.9 |
| Y33 | 410-430 | ≥4100 | 220-250 | ≥2760 | 225-255 | ≥2830 | 31.5-35.5 | ≥4.0 |
| Y33H | 410-430 | ≥4100 | 250-270 | ≥3140 | 250-275 | ≥3140 | 31.5-35.5 | ≥4.0 |
| Y34 | 420-440 | ≥4200 | 200-230 | ≥2510 | 205-235 | ≥2580 | 32.5-36.0 | ≥4.1 |
| Y35 | 430-450 | ≥4300 | 215-239 | ≥2700 | 217-241 | ≥2730 | 33.1-33.2 | ≥4.2 |
| Y36 | 440-450 | ≥4400 | 247-271 | ≥3100 | 250-374 | ≥4400 | 35.1-38.3 | ≥4.4 |
| Y38 | 440-460 | ≥4400 | 285-305 | ≥3580 | 294-310 | ≥3690 | 36.6-40.6 | ≥4.6 |
| Y40 | 450-460 | ≥4500 | 330-354 | ≥4150 | 340-360 | ≥1270 | 37.6-41.8 | ≥4.7 |
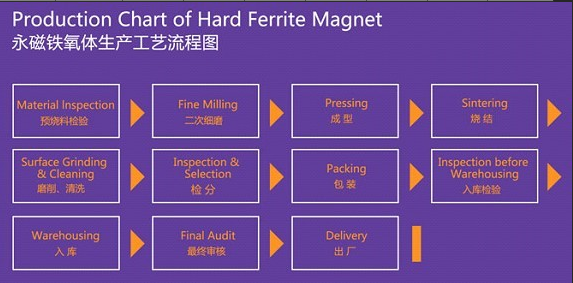
Flow chart
We can provide
1. Best package: Any requirement for package can be satisfied.
2. Fast reply: All your inquiry will be replied within 24 hours.
3. Reasonable price: we are direct manufacturer and able to offer better price.
4. Good quality: we are experienced in quality control.
5. Full-way tracking the cargo for you before the goods arrive.
IN ORDER TO QUOTE YOU THE BEST PRICE, PLEASE PROVIDE US THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION.
| Shape | Block/Rectangle/Square | Disc/Round/Cylinder | Ring/Countersunk |
| Dimension | L (?) x W(? ) xT(?) | D(?) x T(?) | OD(?) x ID(?) x T(?) |
| L: length. W: width, T: thickness, D: diameter, OD: outer diameter, ID: inner diameter.For other shapes, please tell more in details or drawing would be much appreciated. | |||
| Coating | Zn, Nickel, Ni-Cu-Ni, Epoxy, Au, Silver or other ? | ||
| Working Temperature | Normal or High temperature ? | ||
· Customized is Available
· Affordable price
· Quality guaranteed
· T/T and XTranfer accepted
· Other payment accepted
· Fast shipping, Worldwide delivery
· excellent customer service
· Offer free magnetic solution
· Bulk discounts for larger orders
FAQ
What are the key features of ferrite magnets?
Cost-Effectiveness: They are among the most economical types of magnets available. Resistance to Demagnetization: Ferrite magnets have good resistance to demagnetization. Corrosion Resistance: They are highly resistant to corrosion and do not require protective surface treatments. Low Energy Product: While not as powerful as rare-earth magnets (like neodymium), they offer sufficient magnetic strength for many applications.
What are ferrite magnets used for?
Ferrite magnets are used in a wide range of applications, including: Electric Motors and Generators: Particularly in appliances and automotive applications. Speakers and Microphones: Due to their magnetic strength and stability. Magnetic Separators: For separating ferrous materials in recycling and mining operations. Crafts and Hobbies: Such as fridge magnets and various DIY projects. Educational Purposes: For teaching magnetic principles in schools.
How strong are ferrite magnets compared to other types?
Ferrite magnets have lower magnetic energy products compared to rare-earth magnets like neodymium and samarium-cobalt. However, they provide enough magnetic strength for many applications and are preferred when cost is a significant factor or when high magnetic strength is not essential.
Can ferrite magnets be customized?
Yes, ferrite magnets can be shaped and sized during the manufacturing process to meet specific requirements. They are typically formed by pressing in a die, either in a wet (isostatic pressing) or dry (uniaxial pressing) process, and then sintered to achieve their final properties. However, their brittleness limits post-sintering machining to simple grinding processes.
How do you care for ferrite magnets?
Ferrite magnets are quite durable and do not rust, so they require minimal maintenance. However, they are brittle and can chip or break if dropped or mishandled. They should be stored in a dry environment to prevent any possible corrosion of other components or materials attached to the magnets.
Are ferrite magnets affected by temperature?
Ferrite magnets can lose some magnetism permanently at high temperatures, though they have a relatively high Curie temperature (the temperature at which a magnet loses its magnetism) compared to other magnet types. Their magnetic properties begin to degrade at temperatures above 250°C (482°F), but they are suitable for most applications where extreme heat is not a concern.
How are ferrite magnets made?
The manufacturing process involves mixing iron oxide with strontium or barium carbonate, followed by calcining, milling, pressing the powder in a magnetic field to align the particles, and then sintering. The magnets are then magnetized by exposure to a strong magnetic field.
Can ferrite magnets be demagnetized?
Ferrite magnets are resistant to demagnetization but can be demagnetized by exposure to strong opposing magnetic fields, by heating above their Curie temperature, or by physical shock. Under normal conditions, they maintain their magnetism for a long time.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-